1 August 2023
Article
Mobilizing investment in green hydrogen
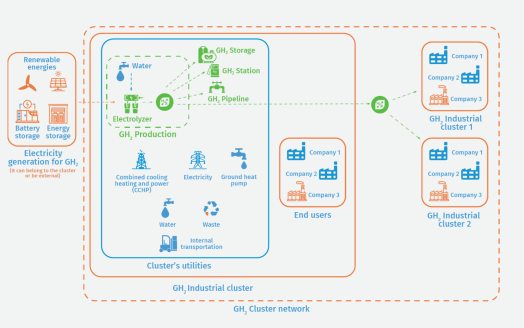
Public policy can be a key driver of green hydrogen (GH2) investment.Source: Mobilizing investment in green hydrogen | Industrial Analytics PlatformDespite its enormous decarbonization potential and recent international efforts, the green hydrogen (GH2) sector is still in the take-off phase, with only about 10 GW in total electrolyser capacity expected to be installed globally in 20231 (see figures below). Most GH2 projects under construction, or in the pre-commercial phase with limited electrolyser capacity—typically less than 50 MW.2 There is also limited market demand for GH2. Due to its high production costs, GH2 cannot yet economically compete with grey hydrogen (produced with fossil fuels), especially in the hard-to-abate steel and cement sectors.3 The absence of a market generates a vicious circle. Low demand deters investment, constraining the GH2 value chain’s efforts to achieve economies of scale, which means prices fail to reach a competitive level. The next figure showcases this price gap, and forecasts how the levelized cost of hydrogen may change for various energy sources between 2019 and 2050.To achieve a breakeven of prices between grey and green hydrogen, an estimated investment gap of about 50 billion US$ needs to be bridged.4 The absence of bankable off-take propositions further contributes to the perception of GH2 projects as risky, and the industry struggles to attract substantial investments. Another major impediment to GH2 investment is the lack of clear, comprehensive regulatory frameworks. This gridlock between investors, developers, policymakers and off-takers must be resolved to kick-start the GH2 value chain.To break this vicious cycle, governments need to address regulatory uncertainty and compensate for the current cost gap, thereby creating a conducive market climate for a GH2 investment take-off. Market & regulatory conditionsLong-term government strategies (e.g. national hydrogen road maps) and concrete commitments regarding GH2’s role in the energy transition can help to create investment security.5 They build the confidence of all stakeholders that there will be a future market for GH2 and related technologies.Permitting for renewable energy generation is a fundamental bottleneck for GH2 adoption, as complex and time-consuming processes can hinder the construction of necessary GH2 facilities and infrastructure.6 Governments can address this issue by streamlining and accelerating these procedures on local and national levels, while ensuring the relevant authorities have the required capacities to process permits for renewable energy and GH2 production sites in a timely manner. Closing the cost gapGreen public procurement is an established policy option to help scale up the value chain through public sector investment.7 Governments can act as a stable initial driver of the demand for final or intermediate green goods produced with GH2. This may particularly promote the creation of a green steel and cement market, as these materials are heavily used in buildings, bridges, railways and other public infrastructure projects.8 In addition to buying directly, governments can offer financial incentives (e.g. subsidies, price premiums or tax rebates) to other end users for the purchase of goods produced with GH2.Acquiring funding for GH2 projects is a particular challenge in developing countries. Foreign investors often take a cautious approach, driven by risk factors such as policy uncertainty, economic instability and low credit ratings. Governments can help to instil investor confidence by offering sovereign guarantees, shifting the risk burden to the public sector if primary obligors default on payments.9 These guarantees can also cover risks that are under government control, such as contractual deviations and tax treatment alterations10. Uncertain prospects in the market for GH2 bring substantial financial risk for the guarantor; any guarantee should therefore be preceded by a thorough assessment of the specific business case. Alternatively, development banks or other donors could step in to act as guarantors for private loans. The Ministry of Finance of a prospective producer country may also issue a “letter of support" document to the project stakeholders, providing enough commitment to comfort them while avoiding the legal robustness of a formal guarantee.11The more regulatory clarity and longevity a state can provide, the more transparent and efficient the interactions between its institutions and private businesses will be – which in turn attracts (foreign) investment. Value chain integration & ecosystem developmentRead the guidelinesA value chain approach is vital for successful interdependent GH2 projects. Public initiatives can create GH2 industrial clusters in optimal geographical locations, concentrating on mobility and industry, with national or international infrastructure support. Identifying suitable cluster development locations, where multiple end users share production and transport, reduces associated costs and risks.12 Government authorities can facilitate consortia of multiple companies along the GH2 value chain, devising solutions for early cluster development.The current absence of an established GH2 financing ecosystem means that projects rely heavily on public funding, often lacking awareness of available alternatives. At the same time, prospective GH2 investors face multiple financing streams with bureaucratic barriers. Establishing centralized digital public matchmaking platforms can reduce this burden and streamline the allocation process.13Until GH2 finance mechanisms and business plans mature, projects like commercial-scale GH2 export and import infrastructure could benefit from public–private partnerships involving direct public investment and multi-stage competitions for contract awards. A modular approach, starting by funding smaller projects to reassure financiers, is an effective way to mitigate risk.14Underlying all of these efforts, governments need to harmonize international standards and eliminate unnecessary regulatory barriers to trade. This is especially important for GH2 transportation, which requires clear regulations for tariffs, safety standards and double taxation. Additionally, a globally agreed definition of GH2 and a standard certification regime will ensure the market recognizes its “green” value.15 Final remarksPublic policy holds a pivotal role in facilitating the large-scale investments that are essential for launching the GH2 economy. They can foster market creation, alleviate regulatory hurdles and shape an ecosystem conducive to private and institutional investments along the entire GH2 value chain. Establishing long-term signals to boost investor confidence, incentivizing investment by reducing risks, stimulating domestic commercial demand for GH2, and harmonizing standards are key strategies to overcome challenges and ensure the successful transition to a GH2-driven future. While global coordination remains essential, it is incumbent on national governments to lead the way in creating a favourable domestic market and investment conditions for the GH2 economy.This opinion piece is a snapshot of the GH2 policy toolkit for developing countries being developed by UNIDO, IRENA and IDOS.Smeeta Fokeer is Industrial Development Officer at the Climate and Technology Partnership Division (CTP) of the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO).Jan Sievernich is Project Associate with the Climate and Technology Partnership Division (CTP) of the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO).Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are those of the authors based on their experience and on prior research and do not necessarily reflect the views of UNIDO (read more). For comparison, the coal power capacity of Germany alone stands at 37.5 GW. World Bank (2022). Blended finance can catalyze renewable energy investments in low-income countries. https://blogs.worldbank.org/ppps/blended-finance-can-catalyze-renewable-energy-investments-low-income-countries KPMG (2022). The hydrogen trajectory. Hydrogen Council (2021). Hydrogen Insights Report 2021. European Investment Bank (2021). Unlocking the hydrogen economy — stimulating investment across the hydrogen value chain. Investor perspectives on risks, challenges and the role of the public sector. IEA (2019). The Future of Hydrogen: Seizing today’s opportunities. Report prepared by the IEA for the G20, Japan. Blaker, A. (2021) Financing the Clean Hydrogen Revolution. Hydrogen Council. IRENA (2022), Green hydrogen for industry: A guide to policy making, International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi. IRENA (2020), Renewable energy finance: Sovereign guarantees (Renewable Energy Finance Brief 01, January 2020), International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi. Griffiths et al. (2021). Industrial decarbonization via hydrogen: A critical and systematic review of developments, socio-technical systems and policy options. IRENA (2020), Renewable energy finance: Sovereign guarantees (Renewable Energy Finance Brief 01, January 2020), International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi. UNIDO (2023) Green Hydrogen Industrial Cluster Guidelines. IRENA (2022), Green hydrogen for industry: A guide to policy making, International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi. IEA (2019). The Future of Hydrogen: Seizing today’s opportunities. Report prepared by the IEA for the G20, Japan. World Bank (2022). Green Hydrogen: A key investment for the energy transition. (Image: Nicholas Doherty via Unsplash)